Mobile:-+91-731-4993339, 4996222 Mail:-admin@pgtech.in
Blog
The Journey of Drug Date-04.03.2020
We get ill due to various reasons and in order to get better, we sometimes get some rest, sometimes be extra cautious with what we eat and other times use medicine.
Some medications are effective directly over the area they are applied to. Some however are transported to distant regions via blood flow and that is where they are most effective. Medication is either taken orally or through injection. When medicine passes into the blood stream from the place of administration, it is considered to be absorbed. A good example is the transportation of medicine into the blood stream of capillary vessels between the muscle cells when injected into muscle tissue. A drug taken orally however is absorbed through the blood vessels in the gastro-intestinal system.

For orally-taken medication to be absorbed, it should be able to dissolve in gastro-intestinal fluids. First, it is broken into smaller units due to the corroding effects of stomach acid and various enzymes are secreted, then chemicals in the drug composition pass into the gastro-intestinal fluid in a molecular form. This event resembles the dissolving of a sugar cube inside a glass of hot tea. First, the sugar cube gets broken into pieces and then dissolves. A mix with a tea spoon makes this event happen a little faster. In a similar fashion gastro-intestinal movements help with the absorption of medicine. Liquid drugs like syrups dissolve in the gastro-intestinal fluid faster since they are already in smaller units; therefore they get absorbed faster.
Drugs mostly get absorbed through the small intestine. The most important task of this organ is to enable the absorption of nutrients. These projections are made of intestinal cells.The molecules carrying the medication reach the capillary vessels by passing through these cells and then join the blood stream by crossing through capillary vessel cells. Furthermore, intestinal cell membranes host a special protein that filters unwanted substances for the cell and returns them back to intestinal lumen. Thus these unwanted substances are excreted out of the body along with other unabsorbed matter. In the same way, some drugs are held by this protein and released back into the lumen thus decreasing absorption rate for drugs experiencing this reaction.
Mrs.Aarti Rajput
PG Tech Research Institute
Medicinal Use of Patharchatta kalanchoe pinnata Date-28/02/2020
Kalanchoe Pinnata or Patharchatta is a succulent perennial medicinal herb which is found almost throughout India. It is small plant which is also used for ornamental purpose in gardens. The plant can easily grow in pots. Patharchatta does not grow from seeds. It propagates from the leaves of the plant and a single leaf can produce 5-10 plants.

Patharchatta is used as a folk medicine in India, tropical Africa, tropical America, China, and Australia. The leaves are used both externally and internally. They have diuretic, wound healing, hepatoprotective, antimicrobial, antihypertensive and anti-inflammatory activities and are beneficial in urinary bladder and kidney stones, intestinal problem, ulcers, arthritis, inflammation, conjunctivitis, menstrual disorders, migraine, urethritis, wound, dysentery, ulcers, indigestion, etc.
Constituents of Kalanchoe Pinnata
Kalanchoe Pinnata contains n-alkane, n-alkanol, alpha- and beta-amyrin and sitosterol.Leaves contain Wax hydrocarbnons, wax alcohols, malic, isocitric and citric acids, glycosides of quercetin and kaempferol, fumaric acid, bryophyllin B and phenolic components.
Important Medicinal Properties
Kalanchoe Pinnata is rich in medicinal properties.
Below is given medicinal properties along with the meaning.
- Astringent: Causing the contraction of the skin cells and other body tissues and helps to stop bleeding.
- Analgesic: Relieve pain.
- Anti-aggregant: Decrease platelet aggregation and inhibit thrombus formation.
- Anti–dysenteric: Relieving or preventing dysentery.
- Anti–inflammatory: Reducing inflammation by acting on body mechanisms.
- Antiseptic: Capable of preventing infection by inhibiting the growth of infectious agents.
- Antispasmodic: Used to relieve spasm of involuntary muscle.
- Cytotoxic: Tending to arrest or prevent cancer
- Diuretic: Promoting excretion of urine/agent that increases the amount of urine excreted.
- Disinfectant: Destroys bacteria.
- Emollient: Soothing and softening effect on the skin or an irritated internal surface.
- Hemostatic: Retarding or stopping the flow of blood within the blood vessels.
- Immunomodulatory: Modifies the immune response or the functioning of the immune system.
- Styptic: capable of causing bleeding to stop when it is applied to a wound.
Mrs Shweta Laad
PG Tech Research Institute
CORONA VIRUSES Date-19.02.20
Corona viruses are found in mammalian and avian species. They resemble each other in morphology and chemical structure. Spherical or pleomorphic enveloped particles containing single-stranded (positive-sense) RNA associated with a nucleoprotein within a capsid comprised of matrix protein. The envelope bears club-shaped glycoprotein projections.

What are corona viruses?
Human coronaviruses (hcov) were first identified in the 1960s in the noses of patients with the common cold. Two human coronaviruses are responsible for a large proportion of common colds OC43 and 229E.Coronaviruses were given their name based on the crown-like projections on their surfaces. “Corona” in Latin means “halo” or “crown.” Among humans, infection most often occurs during the winter months as well as early spring. It is not uncommon for a person to become ill with a cold that is caused by a coronavirus and then catch it again about four months later. This is because coronavirus antibodies do not last for a very long time. Also, the antibodies for one strain of coronavirus may be useless against other strains.
Symptoms
Cold- or flu-like symptoms usually set in from two to four days after coronavirus infection, and they are typically mild. However, symptoms vary from person to person, and some forms of the virus can be fatal.

- Sneezing and runny nose
- Fatigue and cough
- In rare cases ,fever and sore throat
- Exacerbated asthma
Human coronaviruses cannot be cultivated in the laboratory easily, unlike the rhinovirus, another cause of the common cold. This makes it difficult to gauge the coronavirus’ impact on national economies and public health.
There is no cure, so treatments include taking care of yourself and over-the-counter (OTC) medication:
- Rest and avoid overexertion.
- Drink enough water.
- Avoid smoking and smoky areas.
- Take acetaminophen, ibuprofen or naproxen to reduce pain and fever.
- Use a clean humidifier or cool mist vaporizer.
Types
Different types of human coronaviruses vary in the severity of illness they cause and how far they can spread.There are currently seven recognized types of coronavirus that can infect humans.
Common types include:
- 229E (alpha coronavirus)
- NL63 (alpha coronavirus)
- OC43 (beta coronavirus)
- HKU1 (beta coronavirus)
Rarer, more dangerous types include MERS-cov, which causes Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), and severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-cov), the coronavirus responsible for SARS. In 2019, a dangerous new strain started circulating, but it does not yet have an official name. Health authorities are currently referring to it as 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-ncov).
Mrs Aarti Rajput
PG Tech Research Institute
COMPOST AS A FERTILIZER Date-08/02/2020
 Compost, crumbly mass of rotted organic matter made from decomposed plant material which is used for gardening and agriculture Compost is especially important in organic farming, where the use of synthetic fertilizers is not permitted. Compost improves soil structure, provides a wide range of nutrients for plants, and adds beneficial microbes to the soil. The maximum benefits of compost on soil structure (better aggregation, pore spacing, and water storage) and Composts commonly contain about 2 percent nitrogen, 0.5–1 percent phosphorus, and about 2 percent potassium. Nitrogen fertilizers and manure may be added to speed decomposition. The nitrogen of compost becomes available slowly and in small amounts, which reduces leaching and extends availability over the whole growing season. Because of their fairly low nutrient content, composts are usually applied in large amounts.
Compost, crumbly mass of rotted organic matter made from decomposed plant material which is used for gardening and agriculture Compost is especially important in organic farming, where the use of synthetic fertilizers is not permitted. Compost improves soil structure, provides a wide range of nutrients for plants, and adds beneficial microbes to the soil. The maximum benefits of compost on soil structure (better aggregation, pore spacing, and water storage) and Composts commonly contain about 2 percent nitrogen, 0.5–1 percent phosphorus, and about 2 percent potassium. Nitrogen fertilizers and manure may be added to speed decomposition. The nitrogen of compost becomes available slowly and in small amounts, which reduces leaching and extends availability over the whole growing season. Because of their fairly low nutrient content, composts are usually applied in large amounts.
Compost can be prepared on a small scale for home gardens, usually in a simple pile of yard waste and kitchen scraps, though compost bins and barrels are also used. Aeration is important for proper decomposition, so piles are usually mixed every few days. When properly prepared, compost is free of obnoxious odours. A compost pile with the right ratio of carbon to nitrogen (30:1) and with adequate moisture will produce enough heat during decomposition to kill many pathogens and seeds, though it is advisable to avoid adding diseased plant matter and weeds that have gone to seed. Some municipalities collect household yard waste for large-scale composting, which reduces the amount of organic matter in landfills.
Composting parameters
The growing number of papers discussing more issues on composting parameters proves that there is obviously Org. Agr. The various composting parameters, which may not be abundant but are very important to the biochemical processes and for assessing the compost quality. Most of the studied parameters, concern compost monitoring, and compost quality at the end of the process. Fewer studies discuss start-up parameters (C/N ratio, moisture content and particle size of fresh materials).Effective composting can be achieved by providing optimal start up conditions for decomposers. These include proper nutrient balance, moisture content, and aeration. Among these, the nutrient balance is expressed as carbon to nitrogen ratio (C/N ratio). A certain amount of moisture is also essential for composting, since the main site of microbial activity is in the thin water-film on the surface of particles.
C/N ratio
The microorganisms, such as bacteria or fungi, are known to utilize about 30 parts of cellulose for each part of nitrogen in the breakdown process (Choi 1999). Proportions of C and N in composting materials have particular importance. Carbon serving both, as a source of energy and elemental component for microorganisms and nitrogen is essential for the synthesis of amino acids, proteins and nucleic acids. During the active phases of aerobic fermentation, the microorganisms consume 15 to 30 times more carbon than nitrogen. Due to the recalcitrant carbon, which is difficult to degrade, compost of shrub and wood takes longer time to be mature (18 months) than a compost of household waste (with initial C/N of 30) that matures in 7 months. The carbon to nitrogen (C/N) ratio is one of the important factors affecting the composting process as well as the properties of the end-product.
Mrs Aarti Rajput
PG Tech Research Institute
Talc & Ovarian Cancer – Is there a link? Date-9.01.2020
Loiu Slemp, from Virginia said she developed cancer after four decades of daily use of talc-containing products produced by various company specifically Baby powder and Shower to Shower powder. 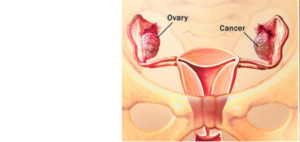 Can Talcum Powder cause Ovarian Cancer?Although it’s almost impossible to prove that any single person’s cancer was caused by something specific. However, in some types of cancer, such as lung cancer, skin cancer and blood cancer there can be a generally accepted link. For e.g. tobacco smoke and asbestos for lung cancer, sunlight or tanning beds for skin cancer, or chemicals such as benzene for blood cancers. Ovarian cancer on the other hand is not common and difficult to link to a generally accepted link also doctors don’t know what causes most cases of Ovarian Cancer.As stated by “The International Agency for Research on Cancer” (IARC), the cancer arm of the World Health Organization, genital use of talc-based body powder is “possibly carcinogenic to humans.”Now, according to various studies conducted around ovarian cancer, there is a mix opinion on whether talc is the only cause of ovarian cancer .British researchers in early 70’s analyzed 13 ovarian tumors under a microscope and found talc particles “deeply embedded” in 10. Further, study conducted in the next decadein the United States and Europe, suggested that women who use talc feminine hygiene products may have up to a 35% higher risk of ovarian cancer than women who don’t make us of those products.Coming back to TalcTalc is mined from soil and is composed of magnesium, silicon, oxygen, and hydrogen. Talc finds its applications in cosmetics and personal care products, such as talcum powder, to absorb moisture, prevent caking and improve the product’s feel. Other uses of talc include manufacture of paints, paper, rubber, roofing and ceramic materials and even as a food additive, a filler in capsules and pills and in cosmetics.Talcum powder might cause cancer in the ovaries if the powder particles (when applied to the genital area or on sanitary napkins, diaphragms) were to travel through the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes to the ovary. Also, study linking the Ovarian Cancer suggests that the risks for epithelial ovarian cancer from genital talc use vary by histologic subtype, menopausal status at diagnosis, HT use, weight, and smoking. Although not concrete, but the observation suggest that estrogen and prolactin may play a role via macrophage activity and inflammatory response to talc.
Can Talcum Powder cause Ovarian Cancer?Although it’s almost impossible to prove that any single person’s cancer was caused by something specific. However, in some types of cancer, such as lung cancer, skin cancer and blood cancer there can be a generally accepted link. For e.g. tobacco smoke and asbestos for lung cancer, sunlight or tanning beds for skin cancer, or chemicals such as benzene for blood cancers. Ovarian cancer on the other hand is not common and difficult to link to a generally accepted link also doctors don’t know what causes most cases of Ovarian Cancer.As stated by “The International Agency for Research on Cancer” (IARC), the cancer arm of the World Health Organization, genital use of talc-based body powder is “possibly carcinogenic to humans.”Now, according to various studies conducted around ovarian cancer, there is a mix opinion on whether talc is the only cause of ovarian cancer .British researchers in early 70’s analyzed 13 ovarian tumors under a microscope and found talc particles “deeply embedded” in 10. Further, study conducted in the next decadein the United States and Europe, suggested that women who use talc feminine hygiene products may have up to a 35% higher risk of ovarian cancer than women who don’t make us of those products.Coming back to TalcTalc is mined from soil and is composed of magnesium, silicon, oxygen, and hydrogen. Talc finds its applications in cosmetics and personal care products, such as talcum powder, to absorb moisture, prevent caking and improve the product’s feel. Other uses of talc include manufacture of paints, paper, rubber, roofing and ceramic materials and even as a food additive, a filler in capsules and pills and in cosmetics.Talcum powder might cause cancer in the ovaries if the powder particles (when applied to the genital area or on sanitary napkins, diaphragms) were to travel through the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes to the ovary. Also, study linking the Ovarian Cancer suggests that the risks for epithelial ovarian cancer from genital talc use vary by histologic subtype, menopausal status at diagnosis, HT use, weight, and smoking. Although not concrete, but the observation suggest that estrogen and prolactin may play a role via macrophage activity and inflammatory response to talc.
Mrs Aarti Rajput
PG Tech Research Institute
TURMERIC OUTSIDE THE KITCHEN
Turmeric has proved its worth in the kitchen time and again. It is more than just a spice, it also has several medicinal values. It contains powerful antioxidants that protect us from aging and some types of cancers. It also facilitates the process of digestion and cleanses the digestive system. And of course, the bright yellow spice brings its own delicious taste to the table when used in the kitchen.

But did you know turmeric works wonders even outside the kitchen? Yes, it doesn’t have to be cooked to be useful to the body. Here are eight ways in which turmeric can be put to use outside the kitchen:
- Skin
Homemade skin care routines consist of turmeric in combination with various other ingredients like milk, cream, curd, sandalwood paste, etc. It cleanses the skin and works well on acne, pigmentation, scars, and stretch marks. Turmeric facial gives a golden glow to the face. - Cold
Home remedies for cold suggest that a teaspoon of turmeric taken with a cup of warm milk can provide relief from symptoms such as cough and sore throat, within hours. - Disinfectant
Turmeric can be used to treat small cuts and wounds. Before covering the wound with Band-Aid, wash it with soap water and apply some turmeric paste. Turmeric leaves are also a good source of curcumin, the anti-bacterial, anti-viral, and anti-inflammatory component of turmeric. Applying the paste of these leaves on burns and cuts helps with the healing process. - Haircare
Dandruff can be treated using a mixture of turmeric and olive oil. Mix both in equal quantities and leave it on the hair for about twenty minutes before washing off with shampoo. - Burns
A mixture of aloe vera gel and turmeric can soothe burns and provide relief by healing them. Skin boils can also be treated by making a thick paste using turmeric and water and applying on the affected area. - Dental care
It is starting to look a little far fetched that a yellow powdery thing can actually be so versatile in its powers, but that is indeed the truth! Using fresh turmeric root (crushed) with coconut oil to clean your teeth at least thrice a week can give you a pearly white set of teeth. - joint
The anti-inflammatory properties of turmeric make it a useful component in home remedies for arthritis pain. Mix turmeric paste with two garlic cloves and one tablespoon honey, and apply over the affected area. Scrape it off after twenty minutes. Repeat this process three times a week and notice the change.
What makes haldi so potent?
The key component of turmeric, Curcumin has many properties that can help in healing and recovery from various ailments. Turmeric has been used as an herbal medicine to help tackle diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, chronic anterior uveitis, conjunctivitis, smallpox, chicken pox, wound healing, urinary tract infections, and liver ailments. It also helps deal with digestive disorders, abdominal pain and distension. Some Haldi health benefits are –

- Anti-Inflammatory –Curcumin has anti-inflammatory properties which can help in reducing inflammation throughout the body. It contributes towards prevention of diseases which are caused due to inflammation. A useful property to deal with achy joints and winter stiffness.
- Antioxidant action –Turmeric also helps promote antioxidant action which aids our bodies in fighting free radicals.
- Improves immunity –Turmeric’s anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties help in fighting infections and ailments such as coughs and colds.
- Better Digestion –It helps in stitmulating the secretion of digestive juices which are essential for proper functioning of the digestive system. A handy feature in case you’ve enjoyed too many of those garam garam parathas and samosas, on a cold winter morning.
Mrs Aarti Rajput
PG Tech Research Institute

